Parthasarathy Temple, Chennai
The Parthasarathy Temple is a 6th-century Hindu Vaishnavite temple dedicated to Vishnu in Chennai, India. Located in the neighbourhood of Thiruvallikeni, the temple is glorified in the Naalayira Divya Prabandham, the early medieval Tamil literature canon of the Alvar saints from the 6th to 9th centuries CE and is classified as among the 108 Divya Desams dedicated to Vishnu.
The name ‘Parthasarathy’ means the ‘charioteer of Arjuna’, referring to Krishna’s role as a charioteer to Arjuna in the epic Mahabharata.
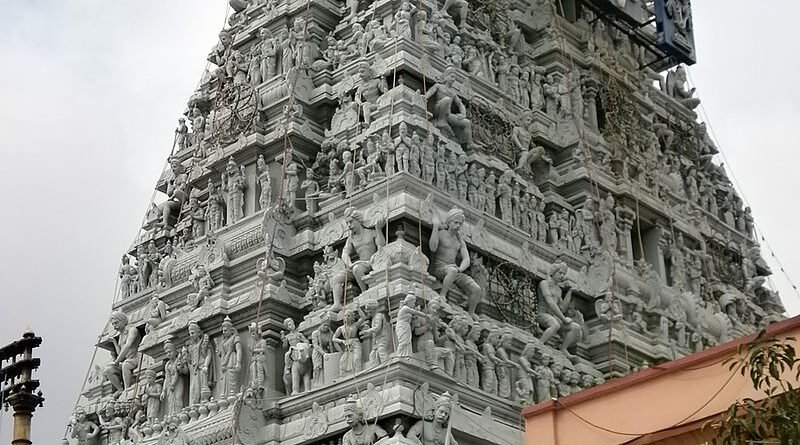
It was originally built by the Pallavas in the 6th century by king Narasimhavarman I. The temple has icons of five forms of Vishnu: Yoga Narasimha, Rama, Gajendra Varadaraja, Ranganatha, and Krishna as Parthasarathy. The temple is one of the oldest structures in Chennai.There are shrines for Vedavalli Thayar, Ranganatha, Rama, Gajendra Varadar, Narasimha, Andal, Hanuman, Alvars, Ramanuja, Swami Manavala Mamunigal and Vedanthachariar. The temple subscribes to Vaikhanasa agama and follows Tenkalai tradition. There are separate entrances and dhvajastambhas for the Parthasarathy and Yoga Narasimha temples. The gopuram (towers) and mandapas (pillars) are decorated with elaborate carvings,a standard feature of South Indian Temple Architecture.
Legend
As per Hindu legend, the Saptarishis, the seven sages worshipped five deities Panchaveeras, namely, Venkata Krishnaswamy, Rukmini, Satyaki, Balarama, Pradyumna, and Aniruddha. As per the Mahabharata, Vishnu, in his avatar as Krishna was acting as charioteer for Arjuna, the Pandava prince during the war with Kauravas. Krishna did not take any weapons during the war. During the fight between Arjuna and Bhishma, Krishna was injured by the arrow from Bhishma. The mark in the image in the temple is believed to follow the legend.The place is called Allikeni, meaning a pond of lily as it is believed that historically the place was full of lily ponds. The place is the only place where the presiding deity is sported with a moustache.As per another legend, the place was once a tulasi forest. A Chola king named Sumati wanted to see Vishnu in the form of Parthasarathy and prayed at Srinivasa temple in Tirupati. Srinivasa directed the king to visit the temple here built by sage Atreya and worshipped with another sage called Sumati.
History
The temple was originally built by the Pallavas in the 8th century, subsequently expanded by Cholas and later by the Vijayanagara kings in the 15th century.tions dating from the 8th century in Tamil presumably from the period of Dantivarman, who was a Vishnu devotee.Thirumangai Alvar, the 9th-century poet-saint also attributes the building of temple to the Pallava king.From the internal references of the temple, it appears that the temple was restored during 1564 CE when new shrines were built.In later years, endowments of villages and gardens have enriched the temple.The temple also has inscriptions about the Pallava king, Nandivarman of the 8th Century.
The temple was extensively built during the Chola period and a lot of inscriptions dating back to the same period are found here. The outer most mandapam is replete with sculptures of various forms of Vishnu, especially the avatars. One can also see inscriptions of Dantivarma Pallava of the 8th century, Chola and Vijayanagara in the temple. The first architectural expansion of the temple took place during the reign of the Pallavas (Tondaiyar Kon) as vividly described by Tirumangai Alvar. Reminiscent of this is the inscription of the Pallava King Dantivarman (796–847 CE), which is preserved in the temple.
The temple witnessed a major expansion during the rule of the Vijayanagara kings like Sadasiva Raya, Sriranga Raya and Venkatapati Raya II (16th century). Many subshrines and pillared pavilions (mandapas) like the Tiruvaymoli Mandapa were added.
A Pallava king built the present temple in the eighth century. The gopuram was also built by a Pallava king – Tondaiman Chakravarthy. There are inscriptions that record the contributions of the Chola kings Raja Raja and Kulottunga III, Pandya King Maravarman and many rulers of the Vijayanagara dynasty including Ramaraja Venkatapathiraja and Vira Venkatapathy. For a while the East India Company administered the temple.
The pushkarani is called Kairavani and five sacred teerthams are believed to surround the tank – Indra, Soma, Agni, Meena and Vishnu. Seven rishis – Bhrigu, Atri, Marichi, Markandeya, Sumati, Saptaroma and Jabali – performed penance here. All five deities in the temple have been extolled by Tirumangai Alvar.
There is also a separate shrine for Andal, one of the 12 Alvars who is also considered as a consort to the presiding deity.
It is one of the very few shrines in the country dedicated to Krishna as Parthasarathy, charioteer of Arjuna and to contains idols of three avatars of Vishnu: Narasimha, Rama, and Krishna.
Unusually, he is depicted with a prominent moustache and carries a conch in his hand. Also unusual is the iconographical combination found in the sanctum. Here, Krishna is seen standing with consort Rukmini, elder brother Balarama, son Pradyumna, grandson Aniruddha and Satyaki. Because of the association of the temple with Krishna, Tiruvallikeni came to be regarded as the Southern Vrindavana. He also mentioned about the Telliya Singar shrine within the temple.
The temple is maintained and administered by the Hindu Religious and Charitable Endowments Department of the Government of Tamil Nadu.